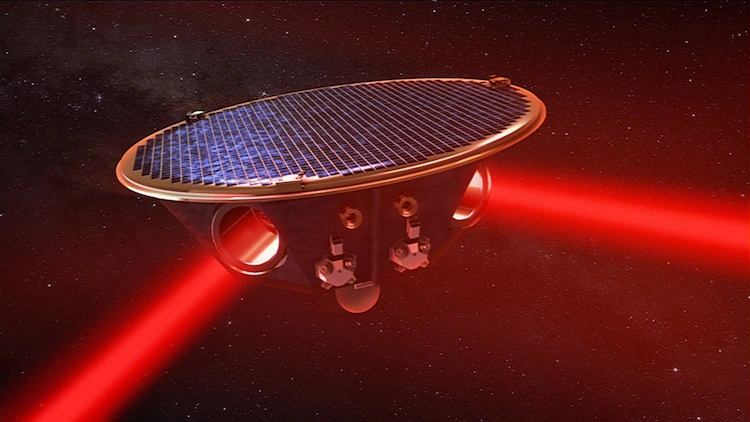
October 22, 2024 – NASA has revealed the first full-scale prototype of six telescopes designed to detect gravitational waves, the ripples in space-time caused by massive cosmic events like merging black holes. This groundbreaking technology is part of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) mission, a collaborative effort with the European Space Agency (ESA), set to launch in the mid-2030s.

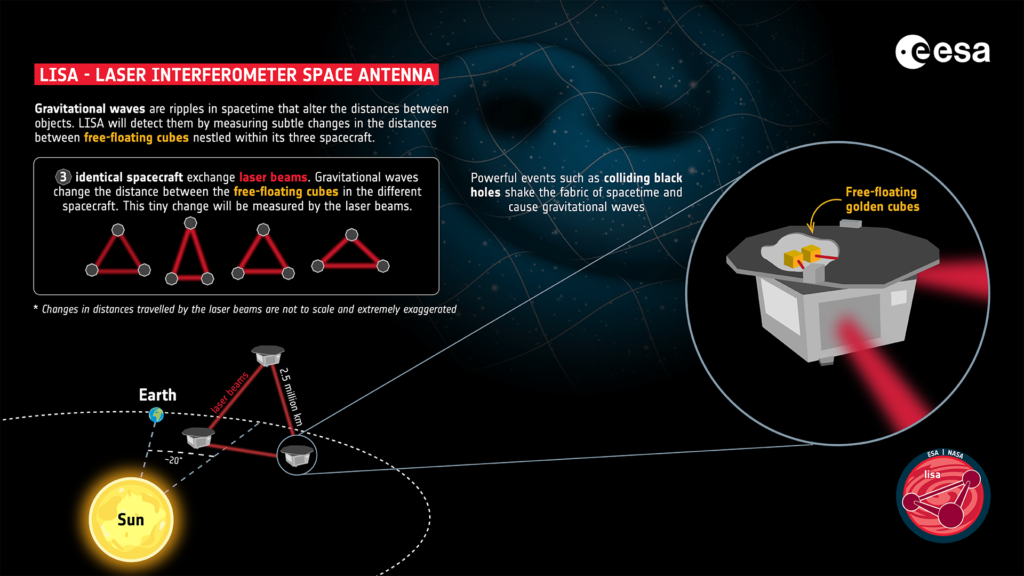
The LISA mission will use an innovative design comprising three spacecraft arranged in a triangular formation, with each side spanning nearly 1.6 million miles (2.5 million kilometers). Twin telescopes aboard each spacecraft will both transmit and receive infrared laser beams, tracking their companions with unparalleled precision. NASA is supplying all six of these crucial components.
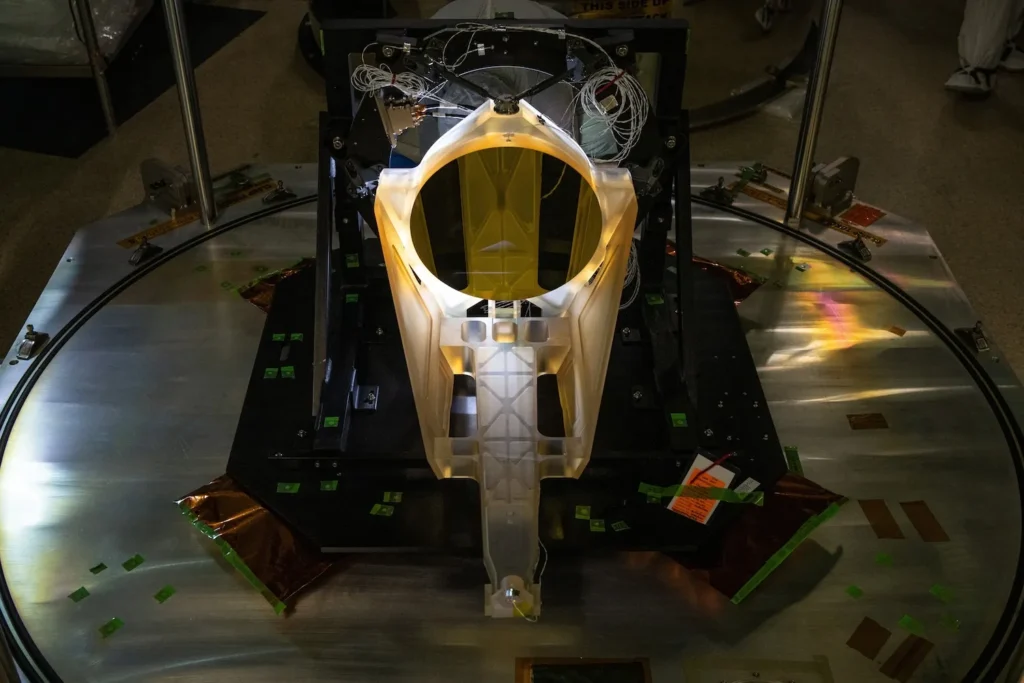
Manufactured by L3Harris Technologies in Rochester, New York, the prototype, known as the Engineering Development Unit Telescope, arrived at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in May 2024. The primary mirror is coated in gold to enhance infrared laser reflection and minimize heat loss in the cold vacuum of space. The telescope is constructed entirely from Zerodur, an amber-colored glass-ceramic renowned for its exceptional thermal stability.
Ryan DeRosa, a researcher at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, explained, “The Engineering Development Unit Telescope will guide us as we work toward building the flight hardware. This prototype will help ensure that the final telescopes can detect gravitational waves with unprecedented precision.”
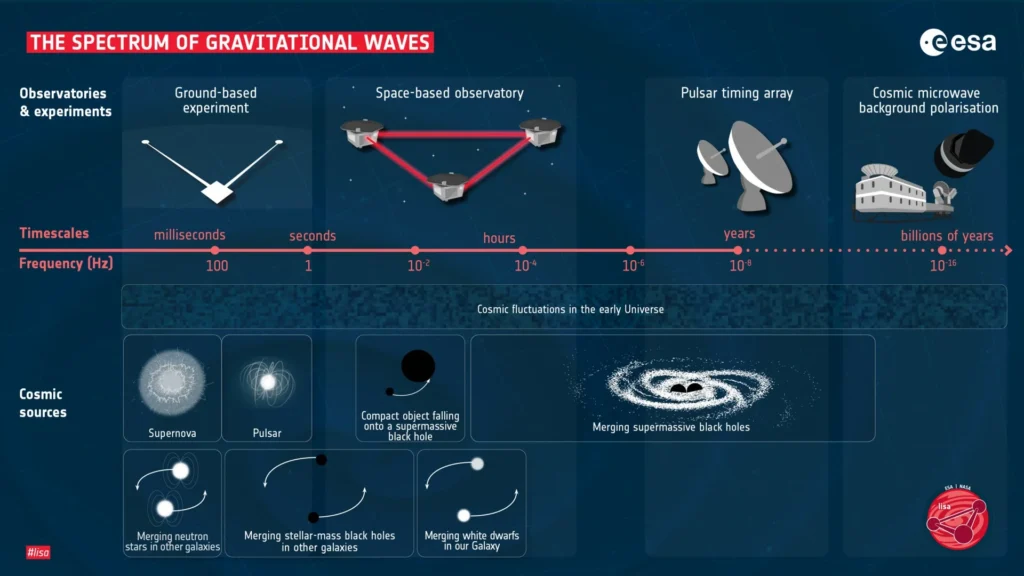
The LISA mission aims to open new avenues for studying the universe by detecting gravitational waves down to picometer scales (trillionths of a meter). This capability will complement traditional astronomical observations, enhancing our understanding of cosmic phenomena.
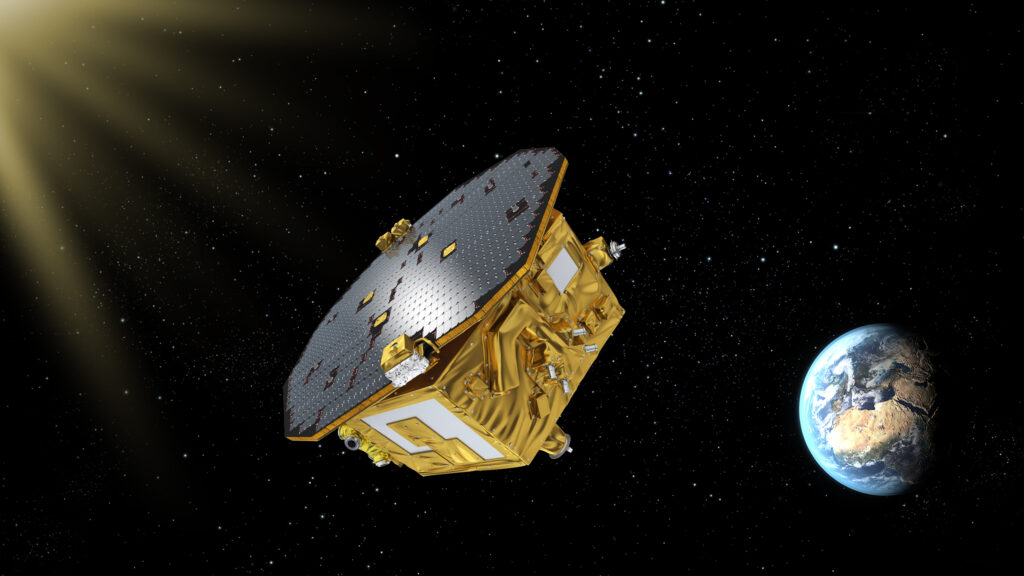

As the LISA mission progresses towards its planned mid-2030s launch, this telescope prototype represents a significant technological achievement, bringing us one step closer to unlocking the gravitational wave universe and revolutionizing our view of the cosmos.